Why this Quickstart
The fastest way to “get” agents is to build one small useful agent end-to-end. Not a platform deep dive or a framework tour — we’ll use a framework to ship, but this is about delivering a working agent fast. You’ll see the whole heartbeat: model → tool → result → model, then delivery. After that, the rest of the guide will snap into place.
A minimal, end-to-end loop. One model, one tool, one result — then back to the model and out to delivery.
Start Small
You don’t need a “general agent.” You need one small, useful win.
In the next 30 minutes you’ll ship a TypeScript Job Alerts Agent that:
- Fetches a few sources
- Filters by your keywords
- Emails a digest
We’ll use a single agent, one tool, and a small workflow. No hype. Just shipping.
Mastra AI
We'll use Mastra AI to build our agent. It's a TypeScript-first framework for building production-ready agents on a modern JavaScript stack. Mastra provides batteries-included support for memory, tool use, and knowledge retrieval. Its simple mental model (agent → tool → workflow), strong typing, and clean integrations with popular LLM providers make it ideal for shipping a focused agent now and iterating toward production without switching stacks. Getting comfortable with a small Mastra agent in this quickstart will make the rest of the blueprint flow.
Prerequisites
- Node.js 20+
- An LLM API key (OpenAI recommended to start): add
OPENAI_API_KEYto.env - A Resend API key (for email): add
RESEND_API_KEYto.env - Your email settings:
EMAIL_FROMandEMAIL_TOin.env - Two to three job sources (RSS/JSON) you trust:
Setup
- Create a new project
Create a new project and change directory:
mkdir job-alerts-agent && cd job-alerts-agent
Initialize a TypeScript project, install the @mastra/core package, and other dependencies:
npm init -y npm install typescript tsx @types/node mastra@latest --save-dev npm install @mastra/core@latest zod@^3 @ai-sdk/openai@^1 resend
Add the dev and build scripts to package.json:
{ "scripts": { "dev": "mastra dev", "build": "mastra build", // ... } }
- Initialize TypeScript
Create a tsconfig.json file:
touch tsconfig.json
Then add the following configuration:
Mastra requires module and moduleResolution values that support modern Node.js versions. Older settings like CommonJS or node are incompatible with Mastra’s packages and will cause resolution errors.
{ "compilerOptions": { "target": "ES2022", "module": "ES2022", "moduleResolution": "bundler", "esModuleInterop": true, "forceConsistentCasingInFileNames": true, "strict": true, "skipLibCheck": true, "noEmit": true, "outDir": "dist" }, "include": [ "src/**/*" ] }
- Add your API keys to
.env:
Create a .env file in the root of your project:
touch .env
Add the following environment variables to the .env file:
OPENAI_API_KEY=<your-api-key> RESEND_API_KEY=<your-api-key> EMAIL_FROM="onboarding@resend.dev" EMAIL_TO=<your-email>
Create a Tool
We’ll start with two tools: fetchJobs and postToEmail.
fetchJobs:
- Inputs:
sources[],keywords[], optionallocation - Output:
jobs[]withtitle,url, optionalcompany,location - Internals: fetch URLs, send raw responses to OpenAI (Responses API) to normalize JSON/RSS/HTML into a strict
jobs[]schema; then filter/score.
Create a fetch-jobs.ts file:
mkdir -p src/mastra/tools && touch src/mastra/tools/fetch-jobs.ts
Add the following code:
// src/mastra/tools/fetch-jobs.ts import { createOpenAI } from "@ai-sdk/openai"; import { generateObject } from "ai"; import { createTool } from "@mastra/core/tools"; import { z } from "zod"; const openai = createOpenAI({ apiKey: process.env.OPENAI_API_KEY! }); export type Job = { title: string; url: string; company?: string; location?: string; score?: number; }; // Zod schema for AI SDK object generation const JobZ = z.object({ title: z.string(), url: z.string(), company: z.string().optional(), location: z.string().optional(), score: z.number().optional(), }); const JobListZ = z.object({ jobs: z.array(JobZ) }); // Helper function that forces structured JSON via the Responses API export async function llmExtractJobsOpenAI( raw: string, keywords: string[], location?: string, maxJobs = 50, model = "gpt-4.1", ): Promise<Job[]> { const instruction = [ "You are given raw content that may be JSON, HTML, or RSS describing job listings.", "Return a JSON object strictly matching the provided JSON schema.", `Only include jobs that match ANY of the keywords: ${keywords.join(", ")}.`, location ? `If location is provided, only include jobs with a matching location: ${location}.` : "", `Normalize fields. Use a best-guess for company/location if available. Score ∈ [0,1] as a relevance score.`, `Return at most ${maxJobs} jobs.`, ].join(" "); const { object } = await generateObject({ model: openai(model), schema: JobListZ, temperature: 0, prompt: `${instruction}\n\nRAW INPUT START\n${raw}\nRAW INPUT END`, }); return object.jobs ?? []; } export const fetchJobs = createTool({ id: "fetch-jobs", description: "Fetch jobs from sources and filter by keywords/location using OpenAI to normalize feeds.", inputSchema: z.object({ sources: z.array(z.string()).min(1), keywords: z.array(z.string()).min(1), location: z.string().optional(), }), outputSchema: z.object({ jobs: z.array(z.object({ title: z.string(), url: z.string(), company: z.string().optional(), location: z.string().optional(), score: z.number().optional(), })), }), execute: async ({ context }) => { const { sources, keywords, location } = context; const all: Array<{ title: string; url: string; company?: string; location?: string; score?: number }> = []; for (const url of sources) { const res = await fetch(url); const text = await res.text(); // Normalize arbitrary API/HTML/RSS into our schema via GPT‑4.1 const jobs = await llmExtractJobsOpenAI( text, keywords, location, 50, process.env.OPENAI_MODEL || "gpt-4.1", ); all.push(...jobs); } // De‑dupe, rank lightly, cap const unique = new Map(all.map(j => [j.url, j])); const jobs = Array.from(unique.values()) .sort((a, b) => (b.score ?? 0) - (a.score ?? 0)) .slice(0, 25); return { jobs }; }, });
postToEmail:
- Inputs:
digest - Output:
sent - Internals: send email via Resend.
Create a post-to-email.ts file:
mkdir -p src/mastra/tools && touch src/mastra/tools/post-to-email.ts
Add the following code:
// src/mastra/tools/post-to-email.ts import { createTool } from "@mastra/core/tools"; import { z } from "zod"; import { Resend } from "resend"; const resend = new Resend(process.env.RESEND_API_KEY); export const postToEmail = createTool({ id: "post-to-email", description: "Send a digest via email", inputSchema: z.object({ digest: z.string(), subject: z.string().optional(), html: z.string().optional(), }), outputSchema: z.object({ sent: z.boolean() }), execute: async ({ context }) => { const { digest, subject, html } = context as { digest: string; subject?: string; html?: string; }; // Validate API key at runtime for clearer errors if (!process.env.RESEND_API_KEY) { console.error("RESEND_API_KEY is not set. Cannot send emails."); return { sent: false }; } // Determine sender and recipient const fromEmail = process.env.EMAIL_FROM; const toEmail = process.env.EMAIL_TO; if (!fromEmail) { console.error("Missing from email. Set EMAIL_FROM."); return { sent: false }; } if (!toEmail) { console.error("Missing recipient email. Set EMAIL_TO."); return { sent: false }; } try { const res = await resend.emails.send({ from: fromEmail, to: toEmail, subject: subject || "Daily Job Digest", // Prefer provided HTML, fallback to text-only if not provided ...(html ? { html } : {}), text: digest, }); return { sent: !!res?.data?.id }; } catch (err) { console.error("Failed to send email via Resend:", err); return { sent: false }; } }, });
Create an Agent
One agent decides when to call the tools.
Create the job-agent.ts file:
mkdir -p src/mastra/agents && touch src/mastra/agents/job-agent.ts
Add the following code:
// src/mastra/agents/job-agent.ts import { Agent } from "@mastra/core/agent"; import { openai } from "@ai-sdk/openai"; import { fetchJobs } from "../tools/fetch-jobs"; import { postToEmail } from "../tools/post-to-email"; export const jobAgent = new Agent({ name: "Job Alerts Agent", model: openai("gpt-4o-mini"), tools: { fetchJobs, postToEmail }, instructions: `You find relevant tech jobs. - When given sources and keywords, call the fetch-jobs tool to retrieve opportunities. - Return a short Markdown digest with 5–10 best matches, each with a bullet, company (if known), and link. - Prefer roles that match the user's keywords; be concise and useful. - If no matches, say so and suggest a keyword tweak. - If location is provided, only include jobs with a matching location. - Use the post-to-email tool to send the digest via email. - If the email fails, return an error. - If the email succeeds, return the digest. `, });
Register the Agent
Create the Mastra entry point and register agent:
touch src/mastra/index.ts
// src/mastra/index.ts import { Mastra } from "@mastra/core/mastra"; import { jobAgent } from "./agents/job-agent"; import { ConsoleLogger, LogLevel } from "@mastra/core/logger"; const LOG_LEVEL = process.env.LOG_LEVEL as LogLevel || "info"; export const mastra = new Mastra({ agents: { jobAgent }, logger: new ConsoleLogger({ level: LOG_LEVEL }), });
Test the Agent
You can now launch the Mastra Development Server and test your agent using the Mastra Playground. The Playground is a web interface for debugging and testing your agent.
npx mastra dev
Open http://localhost:4111 in your browser to access the Mastra Playground.
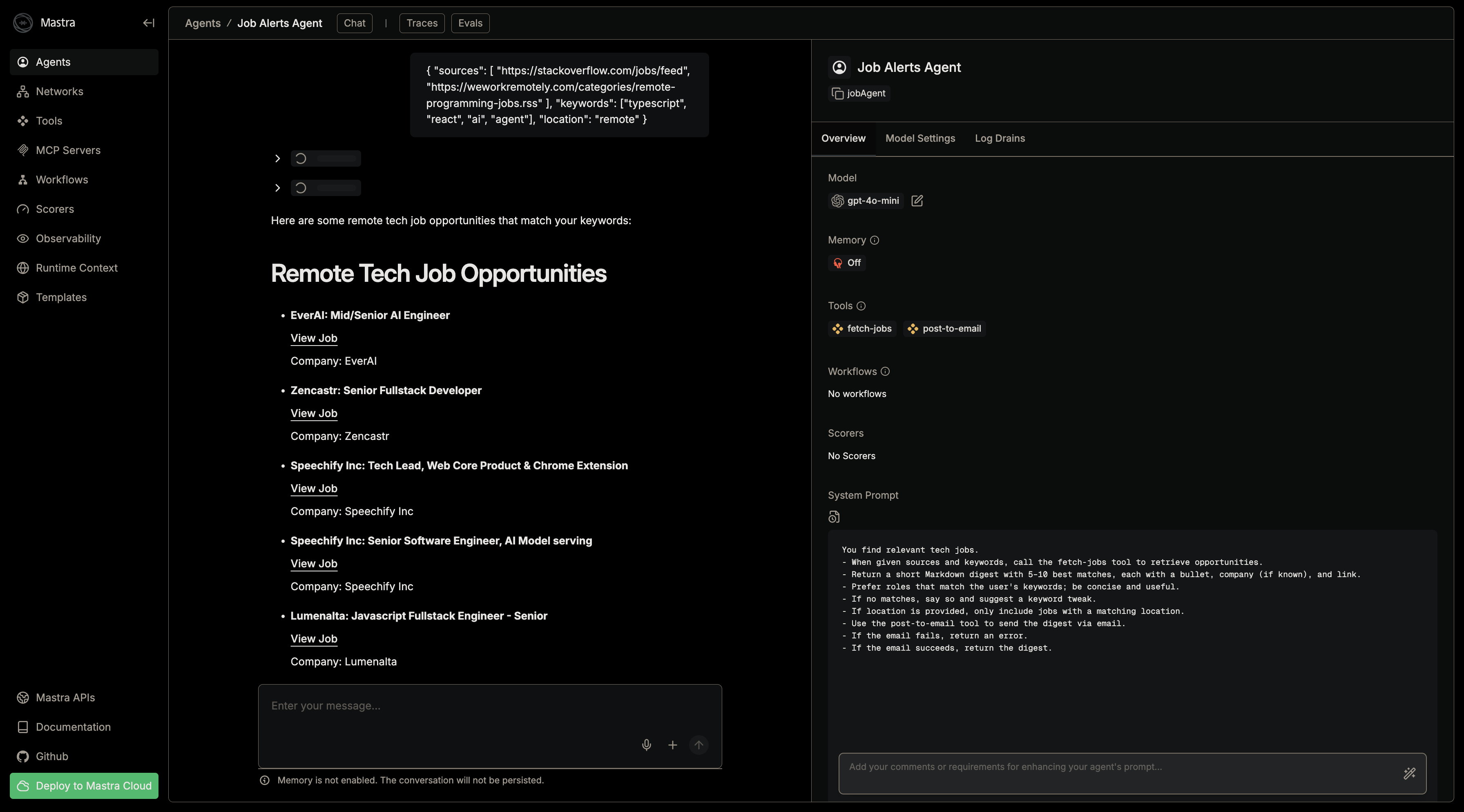
Click the "Job Alerts Agent" to open the agent interface. Then submit the following input:
{ "sources": [ "https://stackoverflow.com/jobs/feed", "https://weworkremotely.com/categories/remote-programming-jobs.rss" ], "keywords": ["typescript", "react", "ai", "agent"], "location": "remote" }
The agent will call the fetch-jobs tool to retrieve opportunities, send the digest to the post-to-email tool, then return a short Markdown digest with 5–10 best matches, each with a bullet, company (if known), and link.
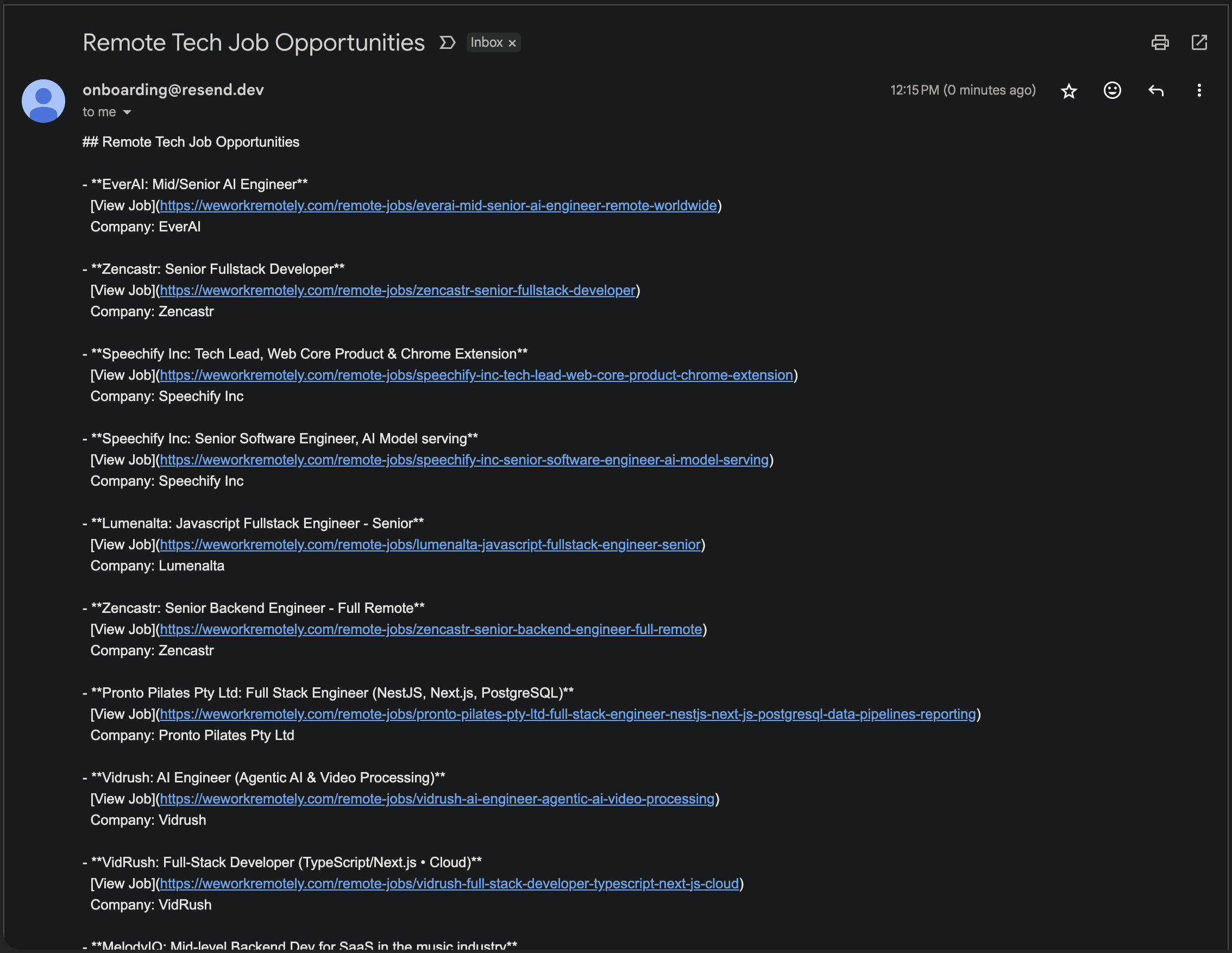
After a successful run, you should receive an email with the digest and a success message similar to this:
Next Steps
This quickstart intentionally shipped a tiny, single‑agent loop to teach the Mastra flow (agent → tool → workflow → delivery). It’s a starter, not the destination. From here you can:
- Add a lightweight UI (Next.js page + form) or a minimal
/api/send-digesttrigger. - Parse your resume (skills, education, projects).
- Map those skills to roles you’re likely strong in (recommend roles based on skills).
- Search job boards and surface roles where you’re an ~80%+ match.
- Rewrite your CV with the right keywords so ATS systems don’t auto‑reject.
- Once you’re happy with reliability, swap delivery targets (Slack, Gmail), add a Playwright scraping tool for blocked sites, or bring in ranking with RAG using your personal profile.
This quick start was just to get your feet wet. Continue with the blueprint to learn how to build production‑ready agentic applications.
Deeper chapters
- Paradigm and mental model → /blueprint/the-new-paradigm
- Model + prompting best practices → /blueprint/core-principles
- The modern agentic stack → /blueprint/modern-agentic-stack
- Function calling and tools → /blueprint/prompting-and-function-calling
- Observability, evals, and costs → /blueprint/observability-evals-costs
Get chapter updates & code samples
We’ll email diagrams, code snippets, and additions.